Breast Cancer Awareness – Malaysian Oncological Society
Breast Cancer is the most common Cancer among women. This form of Cancer has affected thousands of women around the world and yet there is a lack of education about the disease. Hence, this is a simple educational effort presented by the Malaysian Oncological Society to develop breast cancer awareness in conjunction with Pink October 2019. The slides contain easy to understand facts/information that could empower its viewers/readers on battling breast cancer.
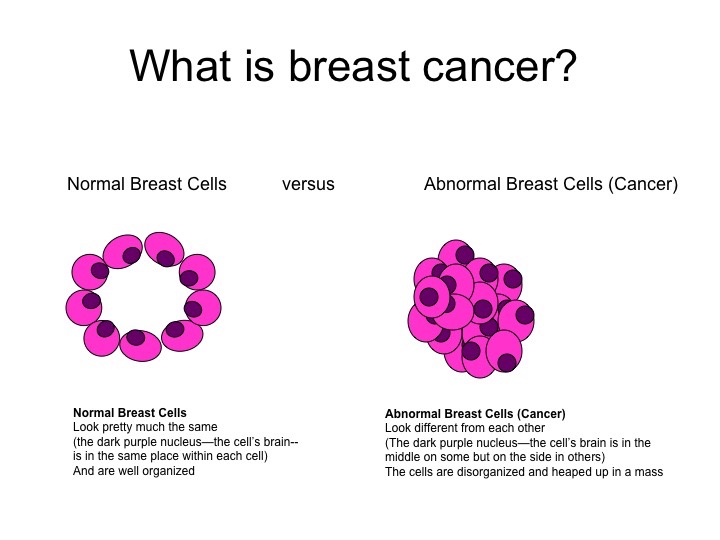
Breast cancer is a disease where malignant (cancer) cells form in the normal tissues of the breast. It occurs when healthy breast cells become abnormal, grow out of control and form a tumour (growth) in the breast. http://triplesteptowardthecure.org/understanding.php
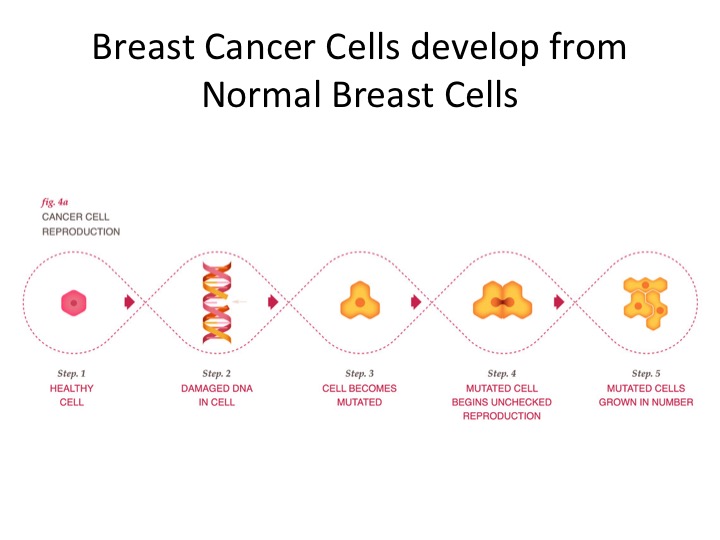
Breast cancer develops from a normal cell in the breast that has acquired many DNA mutations (changes in the genetic signature of the cell) that allows the now abnormal cell to grow out of control and create more cancer cells
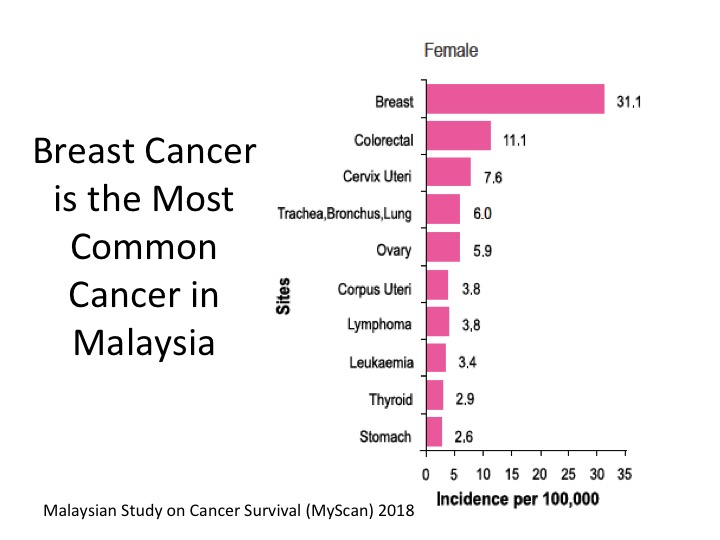
According to the Malaysian National Cancer Registry 2007-2011, breast cancer is the most common cancer in Malaysia with almost a third of all newly diagnosed cancers among Malaysian women. About 3700 women are newly diagnosed with breast cancer every year.
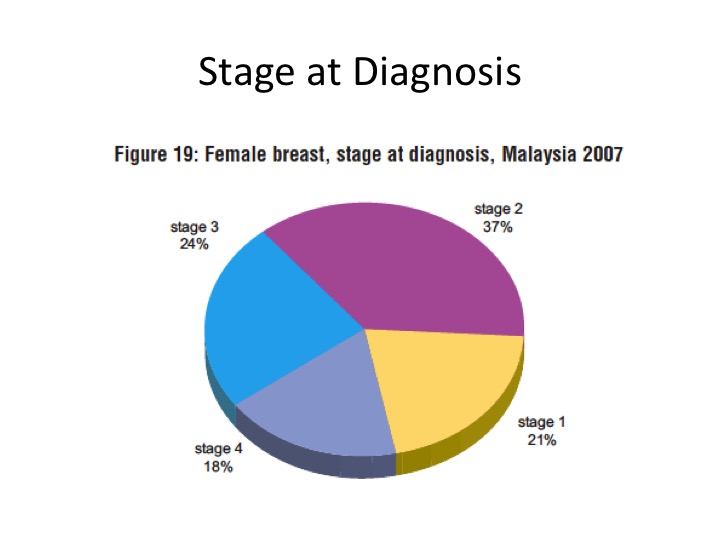
Breast cancer is often diagnosed in a later stage (stage 3 and 4) in Malaysia. This is due to lack of awareness of the signs and symptoms of cancer, fear of cancer, inadequate access to medical care especially in more rural areas of Malaysia.
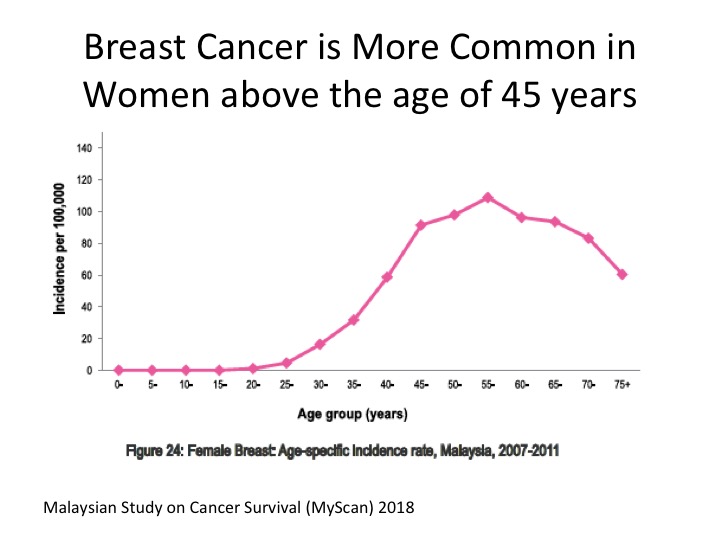
Although breast cancer is more common in women above the age of 45 years in Malaysia, younger women can develop breast cancer too.
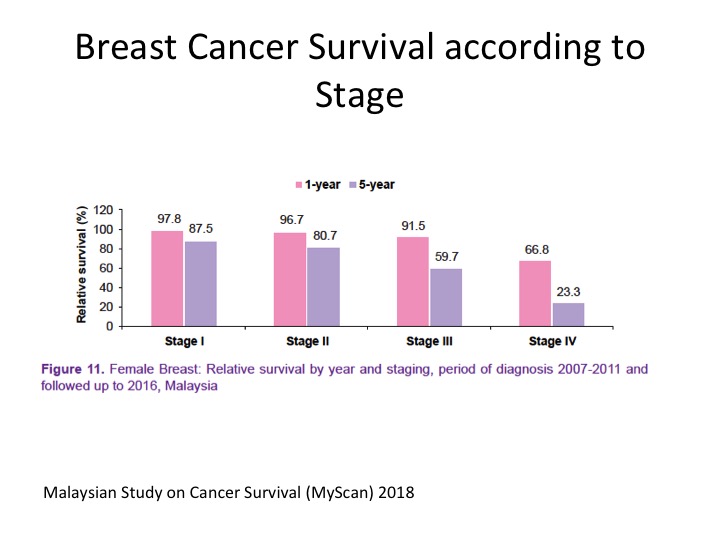
The chance of surviving breast cancer is better the earlier it is diagnosed. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as you notice something abnormal.
An awareness of the risk factors of breast cancer can help you to reduce your exposure to the risks that you can control. If are at higher risk of breast cancer, for example a family history of breast cancer, then you should speak to you doctor or breast surgeon for regular monitoring or screening. www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast
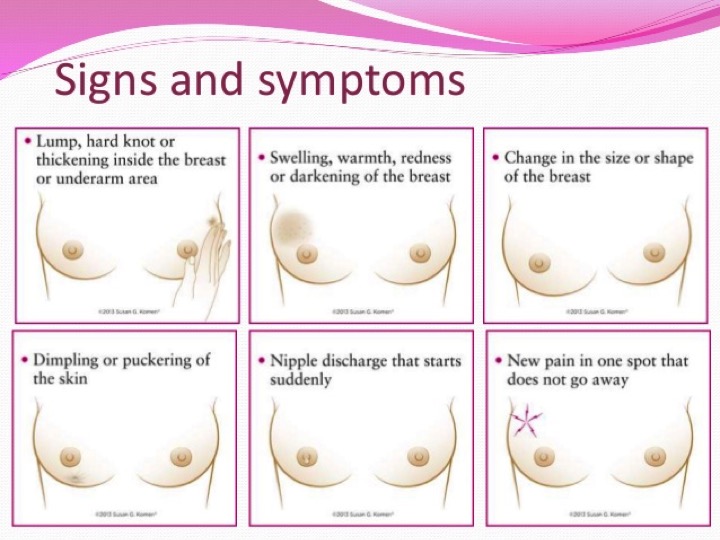
In most cases, these changes are not due to breast cancer. However, it is a good idea to see a doctor for further assessment such as a mammogram or ultrasound scan of the breast. http://www.healthrink.com/signs-symptoms-breast-cancer/
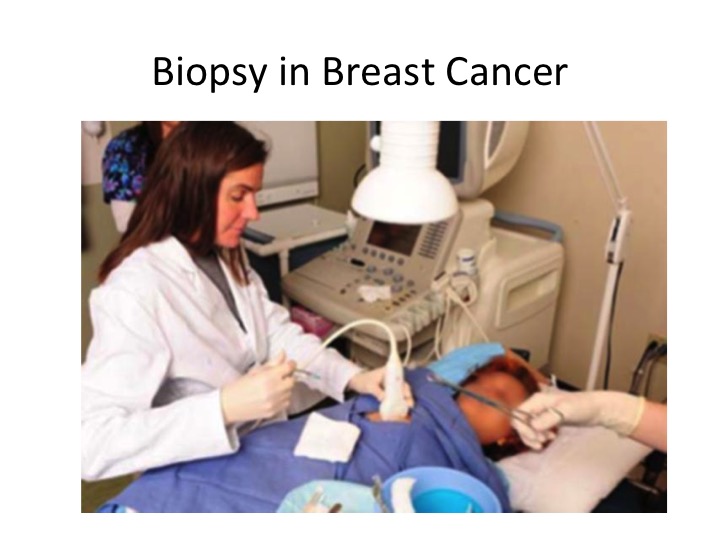
When the mammogram or ultrasound finds something suspicious then it is best to biopsy the breast tumour. Cancer can only be confirmed by finding cancer cells in the tumour and this can only be done in the pathology lab. Therefore, a biopsy is important before any treatment can be planned. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/gallery/index.cfm?image=873
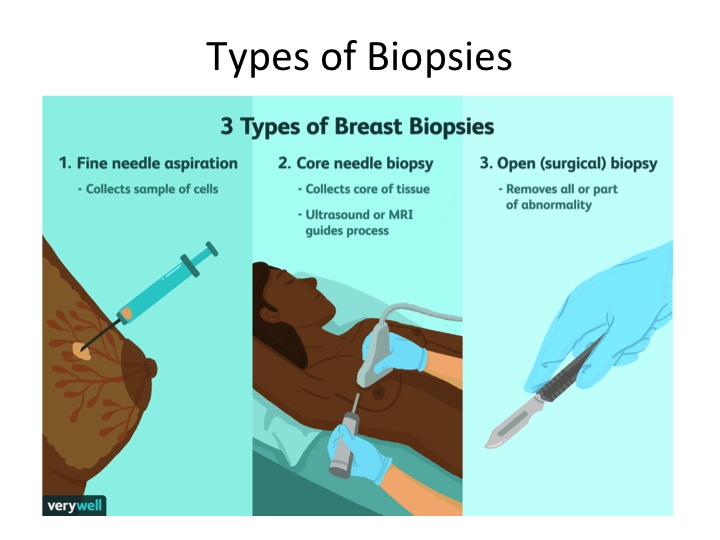
There are three main types of biopsies. The fine need aspiration can often be done during the clinic visit and is used to collect a sample of cells. The core needle biopsy is often done under ultrasound guidance and is able to collect more cells and a bit of tissue. Local anaesthesia may be used during the core needle biopsy. The open biopsy is done under general anaesthesia and the whole breast lump is removed. Illustration by Cindy Chung, Verywell https://www.verywellhealth.com/open-surgical-breast-biopsy-429949
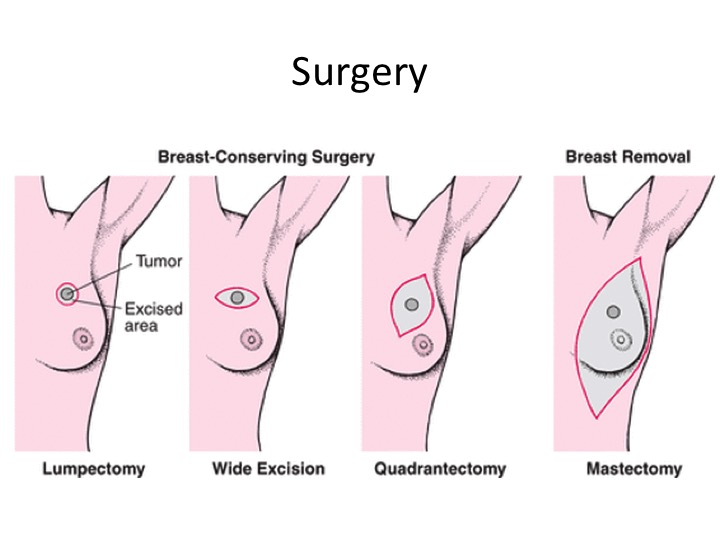
Surgery for breast cancer can be either breast conserving surgery or mastectomy. In a mastectomy, the whole breast, including the skin, is removed. This is usually done in large breast cancers or if the cancer is involving the muscle or skin. In breast conserving surgery, only the breast cancer, including a small margin of normal tissue, is removed and the skin and the normal breast is left intact. Breast conserving surgery is suitable for smaller breast cancers that have not invaded the skin. https://breastcan.weebly.com/surgery.html
A CT scan is often required to check if the cancer has spread to your internal organs. This is important as it will impact the kind of treatment you should have. https://www.macmillan.org.uk/information-and-support/diagnosing/how-cancers-are-diagnosed/tests-and-scans/ct-scan.html
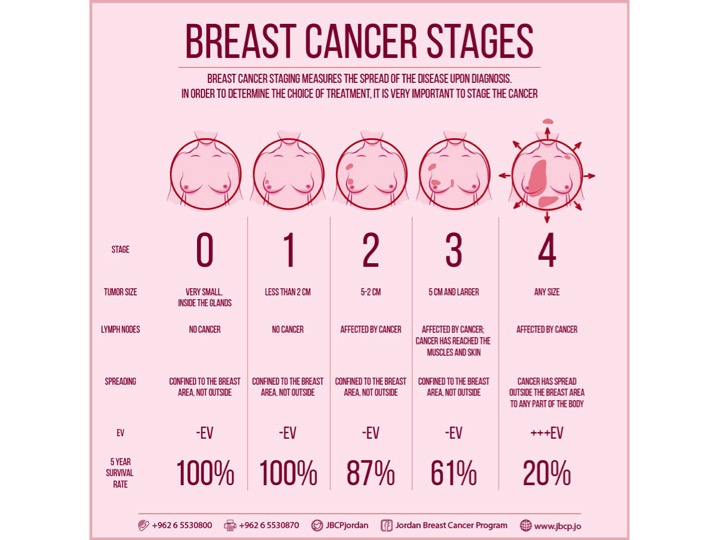
Whether you will need further treatment after surgery will depend on what stage the breast cancer is. The stage of the cancer will also indicate the chance or probability of curing/surviving the cancer. http://www.jbcp.jo/understandingbreastcancer/33
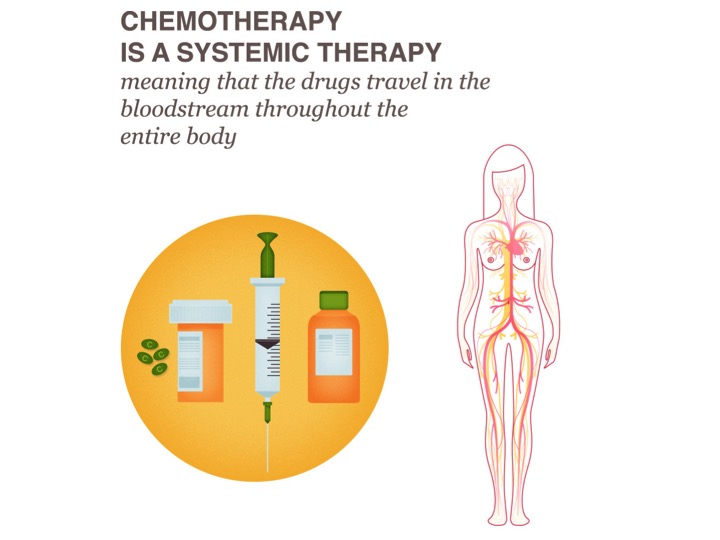
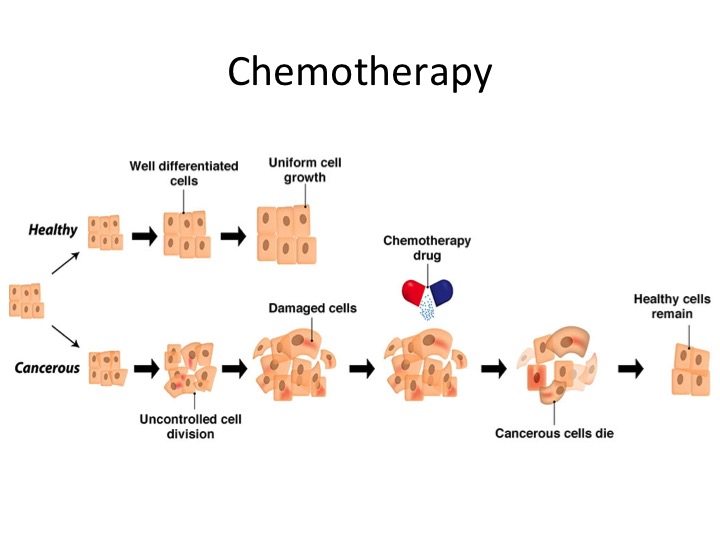
Chemotherapy is often given in patients with early stage breast cancer. This is because surgery alone in these circumstances is usually not sufficient to prevent the cancer from coming back and so chemotherapy is advised to improve the chance of cure. Your oncologist will discuss with you whether you require chemotherapy and how many sessions you need. https://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-cancer-chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is often given in patients with early stage breast cancer. This is because surgery alone in these circumstances is usually not sufficient to prevent the cancer from coming back and so chemotherapy is advised to improve the chance of cure. Your oncologist will discuss with you whether you require chemotherapy and how many sessions you need. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/chemotherapy
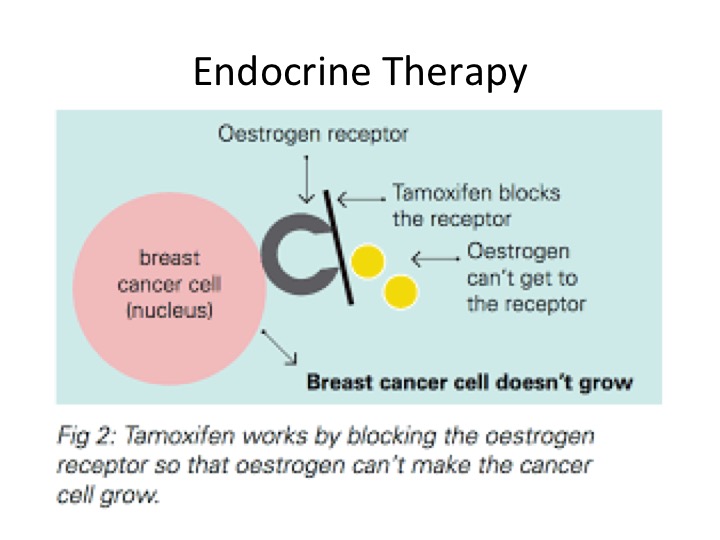
About two thirds of breast cancer are dependent on the female hormones, estrogen and progesterone, to grow. This is because the cancer cells over-express estrogen and progesterone receptors which makes them more sensitive than normal breast cells to the presence of these female hormones. As a result, by blocking the action of these hormones on cancer cells, we can deprive these cells of the stimulus that they need to survive and thus will lead to death of the cancer cells. Endocrine therapy is treatment using medication (usually in tablet form) to block the activity of female hormones on breast cancer cells. https://www.bci.org.au/breast-cancer-information/fact-sheets/hormonal-therapies-breast-cancer/
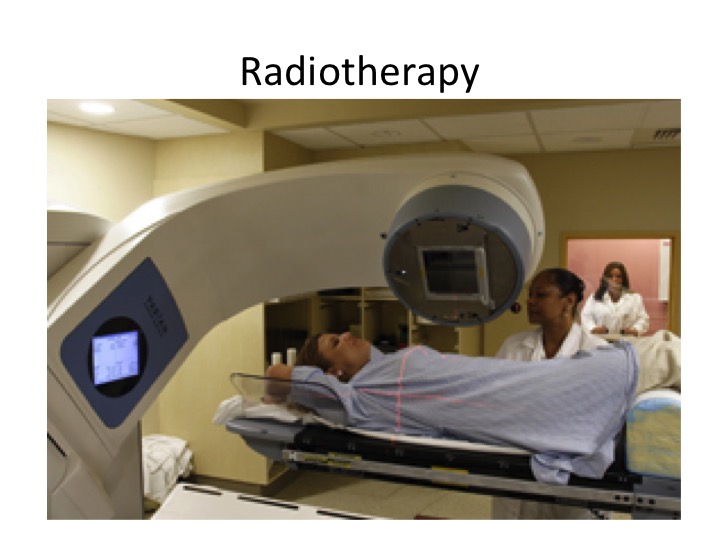
Radiotherapy is the use of X-rays to treat cancers. It is usually given to the whole breast after surgery to prevent recurrence of the cancer in the breast. It is also sometimes given to relieve bone pain or other symptoms due to cancer metastases. https://www.astro.org